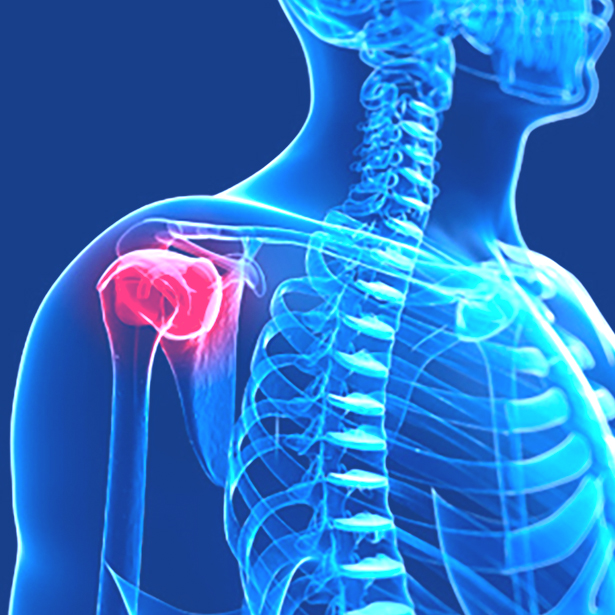
Our treatments provide pain relief for many varing conditions, including;
Rotator Cuff Tendonitis – Front shoulder pain caused by swelling of the shoulder tendons.
Tendonitis – Through repetitive overuse, over strain and aging, tendons can inflamed, which is known as tendonitis.
Impingement Syndrome – Shoulder pain when reaching overhead or behind.
Adhesive Capsulitis – Also known as Frozen Shoulder. Shoulder pain with loss of motion.
Tendonitis
A tendon is a connection of muscle to bone. It is a smooth and strong band that assists movement of limbs through contraction of the muscles. Through repetitive overuse, over strain and ageing, tendons can become worn and weak. This can often cause a tendon to become inflamed, which is known as tendonitis.
What Causes Tendonitis?
Tendonitis is primarily caused by three things; over-use, injury or ageing. In some small number of cases, tendonitis can also be caused by diseases that attack the bones and joints in the body and indirectly cause inflammation of the tendons, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus.
One of the most common causes of tendonitis is overuse injury, primarily in athletes. By consistently pushing your body to its physical limits, the tendons become overused and irritated. This also occurs if a type of exercise is started and tendons that are often inactive become over active and inflamed.
Tendon problems are also common in 40-60 year olds. As the ageing process occurs, tendons lose their elasticity and become more rigid, yet the individual is often exerting the same force on their daily movements. This will also lead to tendons becoming irritated and inflamed.
On rare occasions tendonitis can be caused by anatomical factors. If a tendon does not have a natural path to guide along, it is likely to become irritated and inflamed. This can often occur when an individual experiences a growth spurt. In these infrequent circumstances, surgery may be necessary to realign the tendon.
What are the Symptoms of Tendonitis?
Tendonitis can almost always be diagnosed after physical examination and assessment. The primary symptoms of tendonitis are
– Tenderness directly over the tendon
– Pain with movement of muscles and tendons
– Swelling of the tendon
What are the Different Types of Tendonitis?
Achilles Tendonitis – Achilles tendonitis is one of the more common types of tendonitis, often experienced by athletes and sports people. Symptoms of Achilles tendonitis is pain and swelling in the back of the heel. Early treatment of Achilles tendonitis can help to avoid serious complications such as Achilles tendon ruptures.
Wrist Tendonitis – Wrist tendonitis is identified as pain and swelling around the wrist, caused by inflammation to the tendon sheath. Pain relief can be experienced by rest, ice, immobilise and elevate. Surgery is rarely required.
Posterior Tibial Tendonitis – Posterior Tibial Tendonitis is less common than Achilles tendonitis, but also is located in the foot, primarily on the inner side of the ankle. If posterior tibial tendonitis is left untreated it can result in a flat foot. This is when the arch of the foot collapses and can be very sore after walking or running for long distances.
Patellar Tendonitis – Patellar Tendonitis occurs when there is irritation or inflammation to the patellar tendon, which is located around the kneecap. The common name for Patellar tendonitis is “Jumper’s Knee”. The primary treatment for patellar tendonitis is rest, as it is mainly caused by impact (distance running or consistent jumping).
Rotator Cuff Tendonitis – Rotator Cuff Tendonitis is located in the shoulder and can be caused by a number of varying factors. Tendons in the shoulder can become inflamed and irritated, by overuse in sport, or even by lack of use (eg. long hours of computer work).
Lateral Epicondylitis – Lateral Epicondylitis, more commonly known as Tennis Elbow, is inflammation of the tendons on the outside of the elbow. It is commonly experienced in people who play tennis or golf.
What are the Treatments for Tendinitis?
The most important treatment for tendonitis is; Rest, Ice, Immobilise and Elevate. Tendonitis will get worse the more you use the tendon, so rest is vital.
For individuals involved in sport, it may also be beneficial to get some form of physical therapy, such as Neuromuscular Therapy or Shockwave Treatment of the affected area. These treatments can not only reduce the pain, but also help reduce the inflammation and strengthen the tendon.
While you are getting these treatments you could also ask your therapist about home exercises you can do to increase the strength of specific tendons
